What are Probiotics, their Benefits, Probiotic Supplements and Foods
What are they?
Probiotics are microorganisms, the health benefit of which was proven by evidence-based medicine.
Probiotics are microorganisms, the health benefit of which was proven by evidence-based medicine. Usually the term probiotics refers to bacteria; however the health benefit features may be inherent to other microorganisms such as yeast. In some cases, probiotics are similar to "healthy" bacteria living in a human body, and sometimes they’re the same microorganisms which are found in humans. Most commonly these microorganisms are located in the intestines.
Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria
Most of the "healthy" bacteria fall into one of 2 groups: Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria, although there are many other species of probiotics.
Usually, Lactobacilli are nonpathogenic bacteria taking part in transformation of lactose and other carbohydrates into lactic acid. In humans, they are located in the intestines and vagina forming their microflora. Many strains of Lactobacilli are involved in decomposition of plant food. By producing lactic acid they inhibit pathogenic bacteria and fungi growth. In addition, they improve metabolism.
Along with intestinal mucosa Bifidobacteria protect the intestines against germs and toxins. Also they produce organic fatty acids having high antagonist activity against pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms. Bifidobacteria participate in recycling of food substrates and promotion of parietal digestion, contribute to increase of absorption of calcium, iron and vitamin D as well as generate amino acids, proteins and some vitamins.
Safe use issues
Also a distinction is made between different strains of bacteria, each of them playing different roles in helping your body. Thus, one strain shows effectiveness in improving the immune system, the other one helps in passing of food through the intestines, while the third strain promotes better digestion of some poorly digested substances like lactose. In general, different probiotics perform in different ways – that’s why it’s required to carefully study their effect on the body and to thoughtfully choose them for any intake.
Nowadays probiotics can be found in several forms: as dietary supplements, drugs or probioitic foods
However, you should understand that nowadays probiotics can be found in several forms: as dietary supplements, drugs or probioitic foods. As drugs, probiotics are used in treatment of some diseases alone or in combination with other drugs. In this guise efficiency and safety of probiotics should be proved according to FDA requirements. As dietary supplements, probiotics can be marketed and used without any FDA approval, since the organization just requires corresponding labeling. Thus, probiotic supplements are inappropriate for disease prevention or treatment, but only for maintaining normal functionality of the body.
How do they help?
Although scientists are still not sure how probiotics act, the following health benefits of these microorganisms were found:
- by secreting antibodies to certain viruses they enhance the immune system;
- they produce agents preventing expansion of infections;
- they hinder malignant bacteria attaching to the intestinal walls and inhibit their growth;
- they contribute to growing of the mucus layer in the intestine strengthening the barrier against infection;
- they inhibit secretion or destroy toxins of malignant bacteria;
- by producing B vitamins which are important for metabolism, they prevent anemia and maintain healthy skin and nervous system.
Diseases cured by probiotics

Currently, probiotics are used for the treatment in the following cases:
- acute diarrhea caused by viral, bacterial or parasitic infection;
- antibiotic-associated diarrhea and Clostridium difficile diarrhea;
- diarrhea caused by radiation treatment;
- eradication of Herlicobacter pylori;
- hepatic encephalopathy complications;
- ulcerative colitis;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- constipation;
- postoperative infections prevention;
- lactose malabsorption.
The strongest evidence of their effectiveness is related to the improvement in the intestine functioning as well as to the stimulation of immune system.
Even though there are some promises for using probiotics against atopic eczema, rheumatoid arthritis, high cholesterol and liver cirrhosis, the strongest evidence of their effectiveness is related to the improvement in the intestine functioning as well as to the stimulation of immune system.
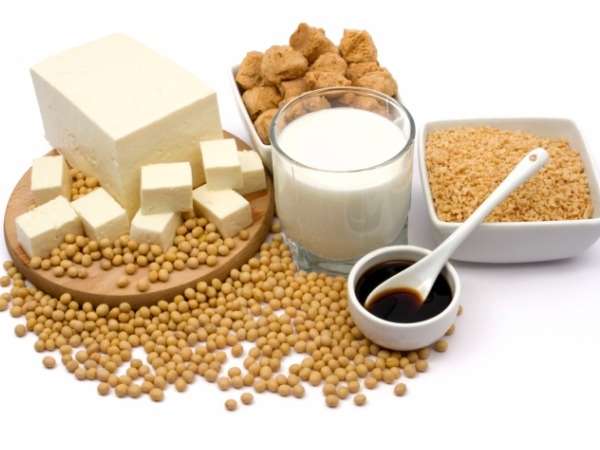
Probiotic foods

Yogurt is a widely-known source of probiotics usually containing Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. It helps maintain healthy microflora in the intestine preventing disorders related to digestion. Yogurt has to contain live and active probiotics, otherwise it won’t have any therapeutic effect.
Sauerkraut is high in vitamins A, B and C, contains Lactic acid and contributes to intestinal microflora balance and, therefore, to proper digestion. Avoid pasteurized sauerkraut in jars, which is usually sold in supermarkets, since the pasteurization kills good bacteria along with the harmful ones. The same is true for pickles, which are a perfect alternative to sauerkraut.
The main ingredient of Japanese miso soup is miso which is a kind of paste produced by fermentation of soybeans, rice, barley, wheat or a mixture of them with the help of a special type of mold. Being low in calories it contains a lot of vitamins and antioxidants as well as over 160 strains of bacteria. Tempeh is also recommended for improving digestion since it’s rich in easily digested protein and due to fermentation contains healthy bacteria. Note, that in Asian food probiotics are usually alive.
Made with the help of mold soft cheeses are considered as useful food, but they may contain too little active probiotics. Some of cheeses, like cottage cheese, are heated in the process of manufacturing, while others, like aged cheeses, lose bacteria during storage.
Kefir is a fermented beverage made from cow's milk and fermented by kefir fungus which consists of about two dozens of lactic acid streptococci and rods, acetic acid bacteria and yeast. Kefir has a positive effect on the intestinal microflora and metabolism in general, inhibits the development of pathogenic flora in the gut, stimulates the immune system and has light diuretic effect.
Acidophilus milk is made with the help of Lactobacillus acidophilus. This bacterium produces milk acid providing high acidity and creating unfavorable conditions for acid-sensitive pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria like staphylococcus, proteus, etc.
Cloudy beer, which wasn’t filtered and heated, is the other great source for probiotics since it contains active yeasts and bacteria. Consumption of cloudy beer from time to time is useful for intestinal microflora – here’s your excuse for drinking your favorite beverage.
Probiotic supplements
Many people find dietary supplements more comfortable, because doses of bacteria in them are better measured and they have a convenient form of administration.
Today on the market there are many probiotic supplements, including capsules, liquids, pills, etc. Many people find dietary supplements more comfortable, because doses of bacteria in them are better measured and they have a convenient form of administration. That's true, but you should understand that when choosing a product, its form is less important than safety and efficiency.
Thus, pay attention to the following information that has to be specified on a label by a manufacturer:
- genus, species and strain of bacteria;
- amount of active bacteria in each dose (Colony Forming Units);
- suggested dose;
- health benefits;
- conditions for storage;
- information about the manufacturer.
Be cautious as probiotics can have a negative effect on the people with compromised immune system, so to get the most health benefit from dietary supplements, it’s better to consult a doctor.
Sources:
http://www.webmd.com/diet/answers-to-your-questions-about-probiotics
http://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/16/11/10-0574_article
http://www.worldgastroenterology.org/guidelines/global-guidelines/probiotics-and-prebiotics
http://www.isapp.net/fermentedfoods
http://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/ss/slideshow-probiotics
http://www.isapp.net/Portals/0/docs/Consumer%20Guidelines%20probiotic.pdf